In-Depth Explanation of All Major Types of Heart Disease
Heart disease is an umbrella term covering various cardiovascular conditions. Below is a detailed breakdown of the major types, including their causes, symptoms, risk factors, treatments, and prevention strategies.
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
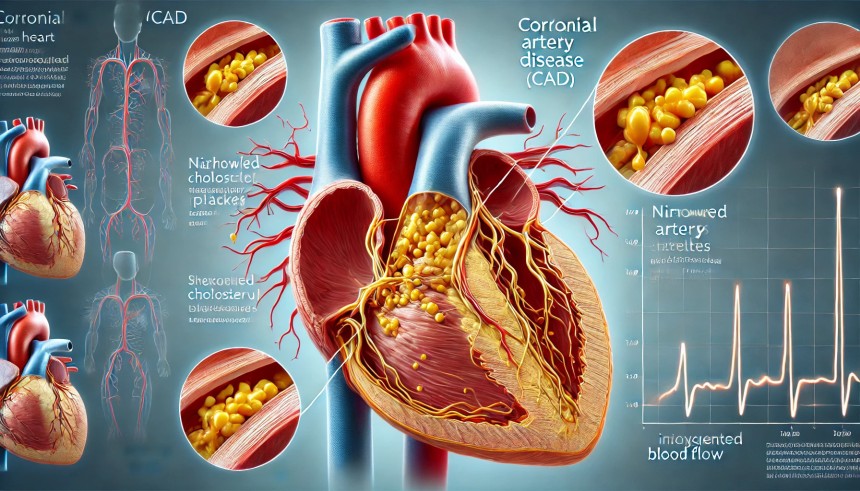
A highly detailed medical illustration of **Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)**, showing a close-up of a human heart with narrowed coronary arteries. The arteries are partially blocked by yellowish cholesterol plaques, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. One section of the image provides a magnified view of the plaque buildup inside the artery, highlighting how it restricts circulation. The background is a semi-transparent anatomical illustration of the heart, with red and blue color coding to differentiate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Labels clearly identify key components, including the coronary arteries, plaque deposits, and restricted blood flow.
What is it?
Coronary artery disease occurs when the coronary arteries (which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart) become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis). This reduces blood flow to the heart and can lead to chest pain (angina), heart attacks, and heart failure.
Causes
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup) – Cholesterol and fatty deposits accumulate in the artery walls.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) – Puts extra strain on the arteries.
- Smoking – Damages blood vessels and increases plaque formation.
- Diabetes – High blood sugar levels can damage arteries over time.
- Obesity – Increases strain on the heart.
- Lack of exercise – Leads to poor circulation and higher cholesterol levels.
- Unhealthy diet – High intake of saturated fats, processed foods, and sugar.
Symptoms
- Angina (chest pain) – Pressure, tightness, or discomfort, often triggered by physical exertion.
- Shortness of breath – The heart struggles to pump enough blood.
- Fatigue – Due to reduced oxygen delivery to muscles.
- Heart attack symptoms – More severe chest pain, nausea, sweating, and dizziness.
Diagnosis
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – Measures electrical activity in the heart.
- Stress test – Assesses heart function during exercise.
- Coronary angiography – Uses X-rays and dye to detect blockages.
- CT scan or MRI – Advanced imaging techniques to assess artery health.
Treatment
- Medications
- Statins – Lower cholesterol levels.
- Beta-blockers – Reduce blood pressure and heart strain.
- Aspirin – Prevents blood clots.
- ACE inhibitors – Help relax blood vessels.
- Surgical Procedures
- Angioplasty and Stenting – A balloon is used to open a blocked artery, and a stent is placed to keep it open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) – A blood vessel is taken from another part of the body and used to bypass the blocked artery.
Prevention
- Adopt a heart-healthy diet (rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins).
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Engage in regular exercise (at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week).
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
2. Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction - MI)
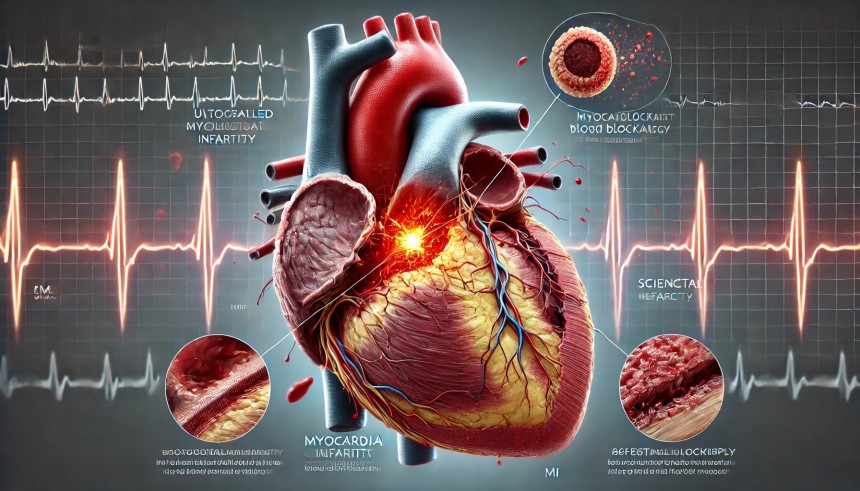
A highly detailed medical illustration of a **Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction - MI)**, showing a close-up of the human heart with a completely blocked coronary artery. The blockage is caused by a ruptured cholesterol plaque, leading to a blood clot that restricts oxygen supply to part of the heart muscle. A highlighted section shows the **damaged heart tissue**, which appears darkened compared to the healthy red muscle. A small inset diagram illustrates the progression of an MI, from plaque buildup to artery blockage and heart muscle damage. The background includes an **ECG waveform**, representing abnormal heart rhythms during a heart attack. Labels clearly identify key components, including the **coronary arteries, blood clot, infarcted tissue, and affected heart regions**.
What is it?
A heart attack happens when blood flow to a section of the heart muscle is blocked, usually by a blood clot. If the blockage isn’t removed quickly, the affected heart tissue begins to die.
Causes
- Atherosclerosis – Plaque buildup can rupture, forming a blood clot that blocks an artery.
- Coronary artery spasm – A sudden tightening of an artery.
- Drug abuse – Cocaine and amphetamines can cause heart attacks.
- Severe stress – Can trigger heart attack-like symptoms.
Symptoms
- Severe chest pain (pressure, squeezing, or burning)
- Pain radiating to the arm, neck, back, or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Cold sweats
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or fainting
Emergency Treatment
- Call 911 immediately.
- Take aspirin – Helps thin the blood and prevent further clotting.
- Nitroglycerin (if prescribed) – Opens up blood vessels.
Medical Treatment
- Thrombolytics ("clot busters") – Break up the clot.
- Angioplasty and stenting – Opens up the blocked artery.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) – Creates a new route for blood to reach the heart.
Prevention
- Manage risk factors like high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Quit smoking.
- Exercise regularly.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet.
3. Heart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure - CHF)
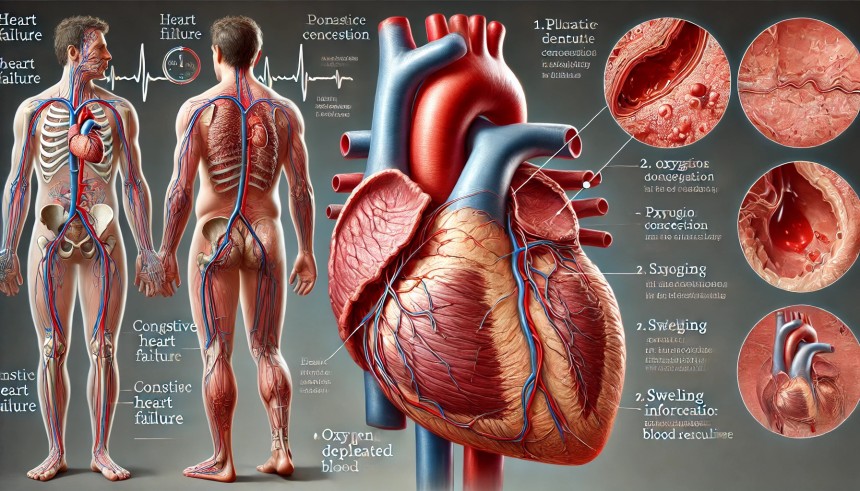
A highly detailed medical illustration of **Heart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure - CHF)**, showing a human heart that is enlarged and weakened. The left ventricle appears dilated and struggling to pump blood effectively. The image includes two smaller insets:
1. **Fluid buildup in the lungs** – Representing pulmonary congestion, with fluid accumulating in the alveoli, making breathing difficult.
2. **Swelling in the legs and feet** – A common symptom of CHF due to fluid retention.
The background features an **oxygen-depleted blood flow diagram**, illustrating reduced cardiac output. Labels clearly identify key components, including the **weakened heart muscle, fluid buildup, and blood circulation issues**.
What is it?
Heart failure occurs when the heart is too weak or stiff to pump blood efficiently, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and body.
Causes
- High blood pressure – Forces the heart to work harder.
- Coronary artery disease – Reduces oxygen supply to the heart.
- Heart attack history – Weakens heart function.
- Diabetes – Damages blood vessels and heart tissue.
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath (even at rest)
- Swelling in legs, ankles, and feet
- Chronic fatigue
- Rapid weight gain (fluid retention)
- Persistent cough with white or pink mucus
Treatment
- Medications: Diuretics (reduce fluid buildup), beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors.
- Lifestyle changes: Low-sodium diet, fluid restriction, daily weight monitoring.
- Surgery: Heart transplant for severe cases.
4. Arrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeat)
A highly detailed medical illustration of **Arrhythmia (Irregular Heartbeat)**, showing a close-up of the human heart with highlighted electrical pathways. The image visually represents different types of arrhythmias, such as:
1. **Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)** – Rapid, chaotic electrical signals in the atria.
2. **Ventricular Tachycardia** – Fast and abnormal impulses in the ventricles.
3. **Bradycardia** – A slow heart rhythm with fewer electrical impulses.
The background features an **ECG waveform**, showing normal vs. abnormal heart rhythms in different sections. Labels clearly identify key components, including the **SA node, AV node, electrical impulses, and irregular heartbeats**. The color-coded pathways visually differentiate **normal and disrupted conduction**.
What is it?
Arrhythmias occur when the heart beats too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregularly (atrial fibrillation).
Causes
- Electrolyte imbalances (low potassium, magnesium)
- Heart disease or damage
- Overuse of caffeine, alcohol, or stimulants
- Thyroid disorders
Symptoms
- Palpitations (fluttering sensation in the chest)
- Dizziness or fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Chest discomfort
Treatment
- Medications (beta-blockers, anti-arrhythmic drugs)
- Pacemakers (for slow heartbeats)
- Ablation therapy (destroys faulty heart tissue)
5. Valvular Heart Disease
A highly detailed medical illustration of **Valvular Heart Disease**, showing a close-up of the human heart with diseased heart valves. The image highlights different types of valvular disorders, including:
1. **Aortic Stenosis** – A narrowed aortic valve restricting blood flow.
2. **Mitral Regurgitation** – A leaky mitral valve allowing blood to flow backward.
3. **Tricuspid Valve Disease** – A malfunctioning tricuspid valve affecting right heart function.
4. **Prosthetic Heart Valve** – A mechanical or biological valve replacement.
The background includes a **side-by-side comparison of healthy vs. diseased heart valves**, showing normal blood flow versus disrupted circulation. Labels clearly identify key components, including the **valve leaflets, narrowed openings, and regurgitating blood flow**. The color-coded pathways visually differentiate **oxygenated and deoxygenated blood movement**.
What is it?
Heart valves control blood flow; if they don’t open or close properly, it leads to leakage (regurgitation) or narrowing (stenosis).
Causes
- Congenital defects
- Rheumatic fever
- Aging-related wear and tear
- Endocarditis (infection of heart valves)
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Chest pain
- Swelling in legs or abdomen
Treatment
- Medications (to manage symptoms)
- Valve repair or replacement surgery
6. Congenital Heart Disease (CHD)

A highly detailed medical illustration of **Congenital Heart Disease (CHD)**, showing a close-up of an infant’s heart with various structural abnormalities. The image highlights different types of congenital defects, including:
1. **Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)** – A hole between the atria, allowing abnormal blood flow.
2. **Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)** – A gap in the ventricular wall, mixing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
3. **Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)** – A combination of four defects causing oxygen-poor blood flow.
4. **Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)** – A persistent open vessel that should close after birth.
5. **Coarctation of the Aorta (CoA)** – A narrowing of the aorta, restricting blood flow.
The background includes a **comparison of a normal vs. CHD-affected heart**, with color-coded pathways to differentiate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood movement. Labels clearly identify key components, including **septal defects, valve abnormalities, and circulation issues**. The illustration is designed in an **educational and professional medical style**.
What is it?
Congenital heart defects are structural heart problems present at birth.
Common Defects
- Septal defects (holes in the heart)
- Valve malformations
- Underdeveloped heart chambers
Symptoms
- Cyanosis (blue-tinted skin)
- Breathing difficulties
- Poor growth and development
Treatment
- Catheter procedures
- Open-heart surgery
- Heart transplant (severe cases)
Heart disease is complex but preventable in many cases. The key is early detection, proper management, and a healthy lifestyle.